
It was previously reported that rutaecarpine produced a sustained hypotensive effect in phenol- induced and two-kidney, one-clip (2K1C) hypertensive animals with a novel antihypertensive mechanism by stimulating the synthesis and release of calcitonin gene e related peptide (CGRP), a principal transmitter in capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerves, and CGRP, in turn, can relax vascular smooth muscle and reduce the peripheral resistance. Rutaecarpine could improve neurological function following injury induced by cerebral ischemia reperfusion, and the mechanism of this improvement may be associated with oxidative stress. Rutaecarpine could significantly decrease the malondialdehyde content and increase the activities of superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase in animal brain. Based on results from a study on the effects of rutaecarpine on myocardial damage, active research concerning the effects of rutaecarpine on cerebral ischemic injury has vital significance and may develop the medicinal value of rutaecarpine.
Therefore, they have common physiological and pathological characteristics, and are very closely related. Vascular lesions occur in both ischemic cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. and then another cup in the afternoon The body processes caffeine in much a similar way as.

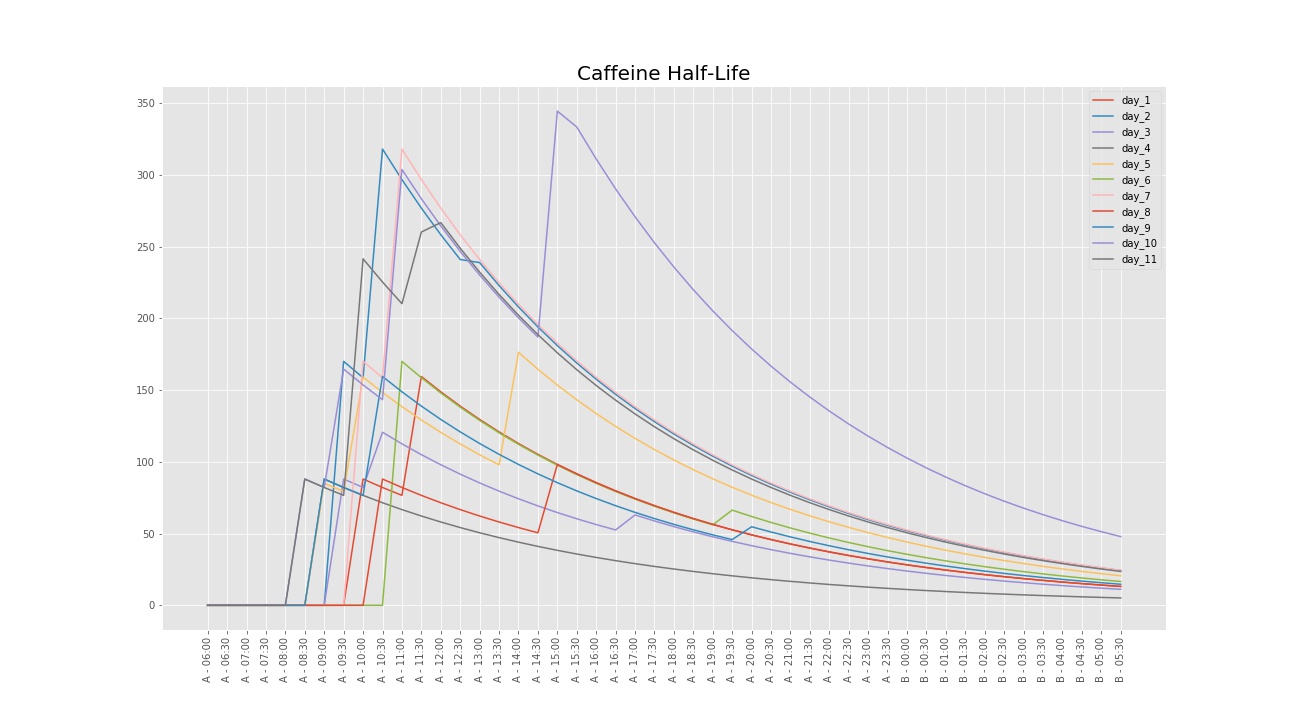
Imagine how that builds up if you have another cup at 10 a.m. The cytochrome P450 (CYP) 1A2 substrate, theophylline, is an important therapeutic agent for the treatment of asthma, but has a narrow therapeutic index. In certain amount of rutaecarpine intravenous injection in animals has a protective effect on heart ischemia reperfusion injury. If your average cup of coffee has 100mg of caffeine and you drink it at 7 a.m., your body metabolizes about half that amount in four to five hours. PMID: 15720787 DOI: 10.1211/0022357055489 Abstract Rutaecarpine is a main active alkaloid present in the medicinal herb, Evodia rutaecarpa. The plant is also touted to reduce pain and gastrointestinal distress, and be anti-cancer. Rutaecarpine protects the heart, relaxes blood vessels, decreases blood pressure, resists platelet aggregation and thrombosis, and also blocks tumor cell growth, inflammation and ulcer formation. Evodia rutaecarpa is the plant which bears the berries evodia fructae (Fruits of Evodia), which are eaten in Traditional Chinese Medicine as a warming technique. It is soluble in alcohol, benzene, chloroform, and ether, but practically insoluble in water. These findings revealed that the methyl group at the N-14 atom of these analogues and their pharmacokinetic behaviors were the main determinants for AHR activation, and suggest that attention should be given to monitoring bile acid metabolism in the clinical use of Euodia ruticarpa.Rutaecarpine is an alkaloid isolated from the fruit of Evodia rutaecarpa and can be synthesized by condensation of iminoketene with amides. Furthermore, RUT, EOD and DHED were not hepatoxic at the doses employed, however, RUT and DHED disrupted bile acid homeostasis in an AHR-dependent manner. In vivo, EOD was poorly orally absorbed and failed to activate AHR, while RUT and DHED markedly upregulated the hepatic AHR battery gene expression in wild-type mice, but not in Ahr-/- mice. Ligand-docking analysis predicted that the methyl substitute at the N-14 atom was a key factor affecting AHR activation. One study showed that the half-life of caffeine in healthy adults is 5. In vitro, both mRNA analysis of AHR target genes in mouse primary hepatocytes and luciferase reporter assays in hepatocarcinoma cell lines demonstrated that RUT, EOD and DHED significantly activated AHR, with an efficacy order of RUT > DHED > EOD. highlights: Rutaecarpine is an ingredient of the plant evodia rutaecarpa. Here, the structure-activity relationships of these analogues for aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) activation were explored by use of Ahr-deficient (Ahr-/-) mice, primary hepatocyte cultures, luciferase reporter gene assays, in silico ligand docking studies and metabolomics. 65 Chinese Journal of Natural Medicines 2011, 9(1): 00650073 Chinese Journal of Natural Medicines Comprehensive Study of Evodia rutaecarpa-induced Contraction on Blood Vascular in Vivo and in Vitro WANG Xiu-Kun 1, 2, WANG Yu-Gang 1, ZHAN Hong-Lei 1, CHAI Yu-Shuang 1, HU Jun 1, XING Dong-Ming 1, YOU Xue-Fu 2, LEI Fan 1, DU Li-Jun 1 1 Protein Science Laboratory of the Ministry of.
Rutaecarpine (RUT), evodiamine (EOD) and dehydroevodiamine (DHED), are the three main bioactive indoloquinazoline alkaloids isolated from Euodia ruticarpa, a widely prescribed traditional Chinese medicine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
